Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has emerged as a valuable non-invasive modality in musculoskeletal care, offering a way to accelerate healing and reduce pain without surgery. Clinicians now routinely use ESWT to manage conditions like chronic tendinopathies and non-union fractures (Moya et al., 2018). Both radial and focused shockwave therapies bring distinct technical features to the table, each affecting treatment depth, precision, and clinical outcomes. For clinics seeking the best shockwave therapy machine for providers, understanding these distinctions is key to selecting the most effective and versatile solution.
Key Differences Between Radial vs Focused Shockwave Therapy
Both radial and focused ESWT share the same fundamental principle of stimulating tissue repair with acoustic energy. Still, they differ markedly in how the shockwaves are generated and delivered into the body. These differences affect how deeply the energy penetrates, the size of the treatment field, and the intensity felt by the patient.
Radial Shockwave Therapy
Radial shockwave therapy, also known as radial pressure wave therapy, generates acoustic waves by using compressed air to propel a projectile that strikes a transmitter at the device’s handpiece. This action produces waves that radiate outward in a broad, divergent pattern.
Due to this dispersion, radial waves exhibit peak intensity at the skin surface, gradually decreasing with deeper penetration, typically effective up to 3–4 cm beneath the skin. Radial shockwaves deliver lower energy levels distributed over a larger area, making them suitable for superficial, diffuse tissues. Additionally, the broader wave coverage generally results in more comfortable patient treatments.
Read more about Radial Shockwave Therapy Machines
Focused Shockwave Therapy
Focused shockwave therapy, in contrast, produces shockwaves using electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, or piezoelectric mechanisms, resulting in waves that concentrate at a precise focal point. Unlike radial waves, focused shockwaves do not disperse widely but rather converge, enabling precise energy delivery to a defined target region.
This focused energy achieves higher penetration depths, reaching approximately 10–12 cm below the skin surface. Due to this concentrated energy, focused shockwaves deliver higher energy flux densities within a localized treatment area, which can lead to increased patient discomfort during treatment. Focused therapy is ideal for precisely targeting deep-seated or localized pathologies that require intense energy delivery to stimulate tissue healing effectively.
Read more about Focused Shockwave Therapy Machines
Clinical Indications for Radial and Focused Shockwave Therapy
Choosing between radial and focused ESWT depends on the tissue depth and the specific treatment goal. While both modalities stimulate healing, certain scenarios favor one modality over the other based on tissue depth and sensitivity.
When to Use Radial Shockwave Therapy
Radial shockwave therapy is best suited for superficial musculoskeletal conditions and broader treatment areas. Its energy dissipates quickly, making it effective for pathologies within a few centimeters of the surface. Radial ESWT has shown strong results in treating chronic plantar fasciitis, significantly reducing pain and improving function in difficult cases (Gerdesmeyer et al., 2008). It is also effective for lateral epicondylitis, with short treatment courses providing notable pain relief and grip strength improvements (Rompe et al., 2004).
Radial therapy’s broader coverage makes it suitable for diffuse tendinopathies and myofascial trigger points. It’s frequently used for conditions like Achilles tendinopathy, where the tissue lies close to the surface. In these cases, studies have shown improved pain and function, particularly when paired with eccentric loading exercises (Moya et al., 2018). Radial ESWT also benefits patients with patellar tendinopathy and greater trochanteric pain syndrome, offering a non-invasive, well-tolerated option for treating chronic soft tissue injuries.
When to Use Focused Shockwave Therapy
Focused shockwave therapy is recommended for deep, localized, or dense tissue targets. Its concentrated energy makes it ideal for addressing issues like calcific tendinitis of the shoulder, where calcium deposits limit mobility and cause pain. Focused waves can fragment and promote resorption of these deposits, with studies reporting significant pain reduction and improved function (Ioppolo et al., 2013). Focused ESWT is also effective in promoting calcification resorption within six months in many cases.
It’s a preferred option for nonunion fractures and early-stage avascular necrosis of the hip, stimulating bone healing and revascularization without surgery (Moya et al., 2018). Focused shockwaves are also used in sexual medicine to treat vasculogenic erectile dysfunction, reaching deep vascular tissues to trigger neovascularization (Wu et al., 2020). Overall, focused ESWT is most appropriate for deep-seated pathologies requiring targeted, high-energy delivery.
Radial vs Focused Shockwave Therapy Compared
To guide clinical decisions clearly, the following table briefly compares the primary features of radial and focused shockwave therapies:
| Aspect | Radial Shockwave Therapy | Focused Shockwave Therapy |
| Energy Levels | Lower | Higher |
| Penetration Depth | Shallow (3-4 cm) | Deep (up to 12 cm) |
| Treatment Area | Broad, superficial regions | Localized, precise areas |
| Patient Comfort | Generally more comfortable | May cause discomfort due to higher energy |
| Session Duration | Typically shorter | Variable, condition-dependent |
This comparative framework aids clinicians in choosing the modality best aligned with specific patient presentations and therapeutic goals.
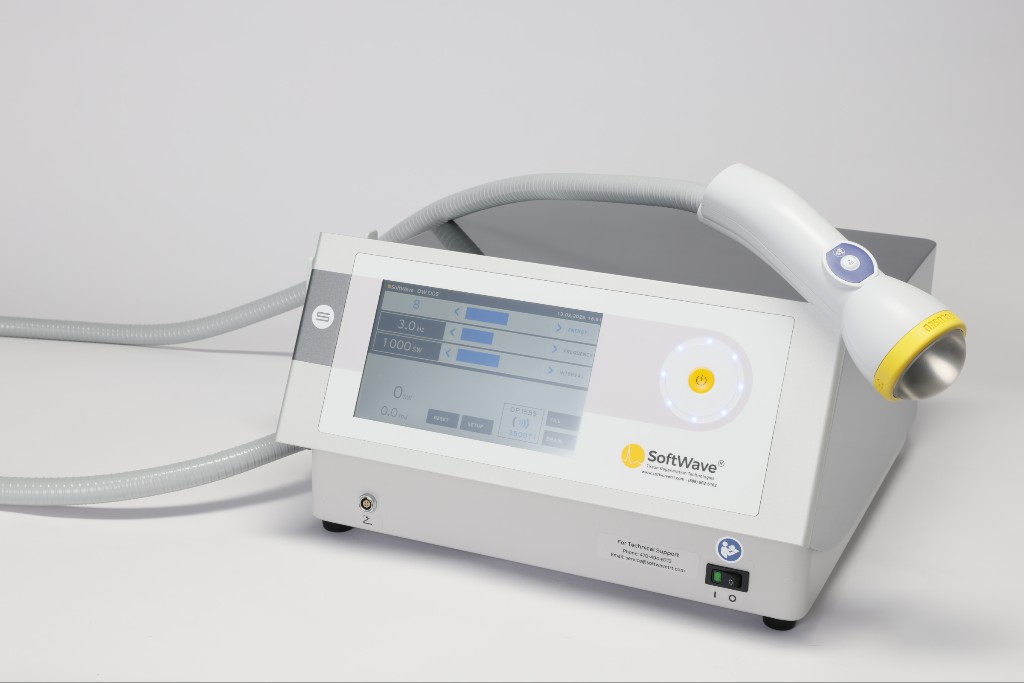
Introducing SoftWave Therapy and Its Advantages Over Traditional Shockwave Modalities
While radial and focused shockwave therapies each offer specific advantages, SoftWave Therapy offers a versatile solution. SoftWave stands out from traditional ESWT devices through its patented, broad-focused applicator technology that uniquely enables treatment of both superficial and deep tissues simultaneously. Utilizing a patented parabolic reflector, SoftWave creates a parallel acoustic wave distribution without causing microtrauma, thus optimizing therapeutic outcomes while maintaining patient comfort.
SoftWave therapy effectively modulates inflammation, increases local blood supply, and promotes angiogenesis by stimulating cytokines and growth factors. These biological responses result in accelerated tissue regeneration, wound epithelialization, and significant pain relief, making it suitable for an extensive range of medical specialties, including orthopedics, sports medicine, physical therapy, urology, and podiatry.
The technology behind SoftWave is FDA-cleared and Health Canada Licensed, indicating its recognized safety and effectiveness. With 10-minute treatment sessions, clinicians can efficiently enhance patient throughput while achieving remarkable clinical outcomes. Patients commonly report quick recovery times and notable improvements after just a few sessions.
Review the newest clinical research behind SoftWave’s efficacy.
Elevate Your Practice with SoftWave Therapy
Understanding the nuanced differences between radial and focused shockwave therapy can significantly enhance clinical decision-making, enabling providers to tailor treatments to each patient’s specific needs. SoftWave Therapy represents a significant advancement in shockwave technology, delivering optimized energy distribution, enhanced patient comfort, and superior clinical outcomes. If you aim to expand your therapeutic options, increase patient satisfaction, and generate robust practice growth, consider integrating this innovative modality.
Become a SoftWave Provider and schedule your demo today.